Methods to Install Android 13 Beta 3.3 on Google Pixel Phones
Google has delivered one more variant of Android 13 Beta 3, the Android 13 Beta 3.3. A few issues have …

Google has delivered one more variant of Android 13 Beta 3, the Android 13 Beta 3.3. A few issues have …

All of you know that the gaming cell phone should have a good quality processor. Even though when we discuss …
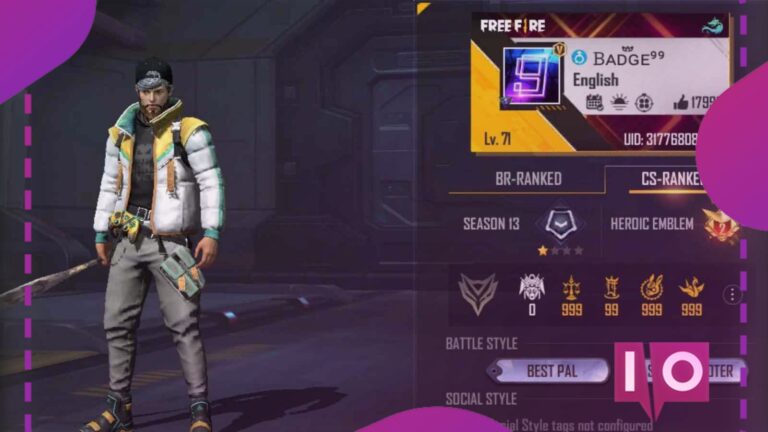
Players who play more in positioned mode generally attempt to keep their details decent. That incorporates a high KD proportion …

WhatsApp these days has turned into a need for us, at the point when we need to contact our companions …

On the off chance that you appreciate watching motion pictures and TV appears through web-based features while dealing with your …

Apple has a program back to School where you really want to enlist your Student ID, and you will need …

In case you have as of late moved from Android to iOS, you likely faced a couple of issues dividing …

A smartwatch is only a tiny PC that gives it capacities inside a conventional watch. Because of its different benefits …

iOS 16, the most recent variant of the iOS, was uncovered at WWDC 2023 with plenty of new highlights. This …

On the off chance that you are a convenient gamer, you may not be content with your phone’s continuous gaming …